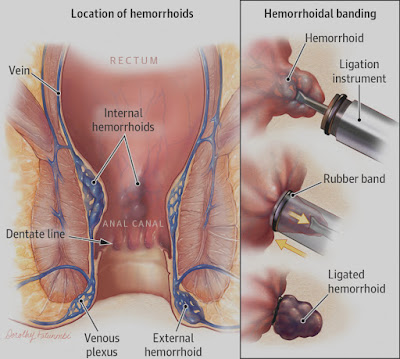
Hemorrhoids (or hemroids) are also known as piles. Although they can be extremely unpleasant and painful, they can be easily treated and are very preventable.
As hemorrhoids generally get worse over time, doctors suggest that they should be treated as soon as they appear.
It has been suggested that up to 75 percent of adults in Europe and North America will experience hemorrhoids at some point in their lives.
Approximately 50 percent of those people aged 50 years and over will require treatment. However, it is striking that only around 4 percent actually seek medical treatment.
Hemorrhoids are most common among adults aged 45-65. This does not mean, however, that young people and children do not get them. Hemorrhoids are much more common among men than women. A woman is most likely to get them when she is pregnant.
Causes of pile.
Constipation, too much carbohydrate, chronic diarrhea,
lifting heavy weights, pregnancy or straining when passing a stool.
The tendency to develop hemorrhoids may also be inherited. The risk of developing piles grows with age.14
Symptoms of piles
In most cases piles are not serious and go away on their own after a few days.
An individual with piles may experience the following symptoms:
A hard lump may be felt around the anus. It consists of coagulated blood, called a thrombosed external hemorrhoid. This can bepainful.
After going to the toilet, a feeling that the bowels are still full
Bright red blood after a bowel movement
Itchiness around the anus
Mucus discharge when emptying the bowels
Pain while defecating
The area around the anus may be red and sore.
Treatments for piles
In the majority of cases, piles resolve on their own without the need for any treatment. Treatments can help significantly reduce the discomfort and itching that many patients experience.
A good doctor will initially recommend some lifestyle changes.
Diet - piles can be caused by too much straining when doing bowel movements, which is the result of constipation. A change in diet can help keep the stools regular and soft. This involves eating more fiber, such as fruit and vegetables, or switching your cereal breakfast to bran.16
Water is the best drink, and the patient may be advised to increase his/her water consumption. Some experts say too much caffeine is not good.
Body weight - if the patient is obese, losing weight may help reduce the incidence and severity of hemorrhoids.
Simple things you can do yourself to help prevent piles:
Try not to strain when you go to the toilet
Avoid laxatives
Exercise.
Ointments, creams, pads and other OTC medications - there are some over-the-counter (OTC) medications which help soothe the redness and swelling around the anus area. Some of them contain witch hazel, hydrocortisone, or some other active ingredient which can relieve symptoms of itching and pain.
It is important to remember that they do not cure piles, they only treat the symptoms. Do not use them for more than seven consecutive days - longer periods may irritate the anus area and cause skin thinning. Unless advised to by your doctor, do not use two or more medications simultaneously.
Painkillers - ask your pharmacist for suitable painkilling medications, such as acetaminophen (Tylenol).
Surgery - used for particularly large piles, or grades 3 or 4 hemorrhoids. Generally, surgery is used if other procedures were not effective. Sometimes surgery is done on an outpatient basis - the patient goes home after the procedure.
Hemorrhoid stapling - blood flow is blocked to the tissue of the hemorrhoid. This procedure is usually less painful than hemorrhoidectomy. However, there is a greater risk of hemorrhoid recurrence and rectal prolapse (part of the rectum pushes out of the anus).
Complications linked to piles
Anemia - hemorrhoids can sometimes cause long-term blood loss, which may lead to anemia.
Stangulated hemorrhoid - the blood supply to an internal hemorrhoid is cut off, causing severe pain, and even gangrene (death of tissue).
In other to be fully safe from try and error treatment and surgical operation, we strongly recommend OZEM Super Boost, a multi-purpose natural health drink.
Hemorrhoids: Facts, Causes, and Treatments
 Reviewed by King Life
on
December 15, 2016
Rating:
Reviewed by King Life
on
December 15, 2016
Rating:
 Reviewed by King Life
on
December 15, 2016
Rating:
Reviewed by King Life
on
December 15, 2016
Rating:


No comments: